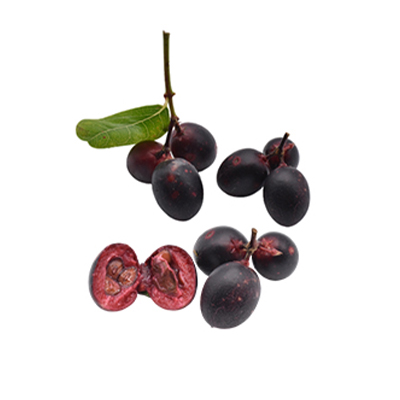
Buah Renda
Carissa carandas L.
Apocynaceae
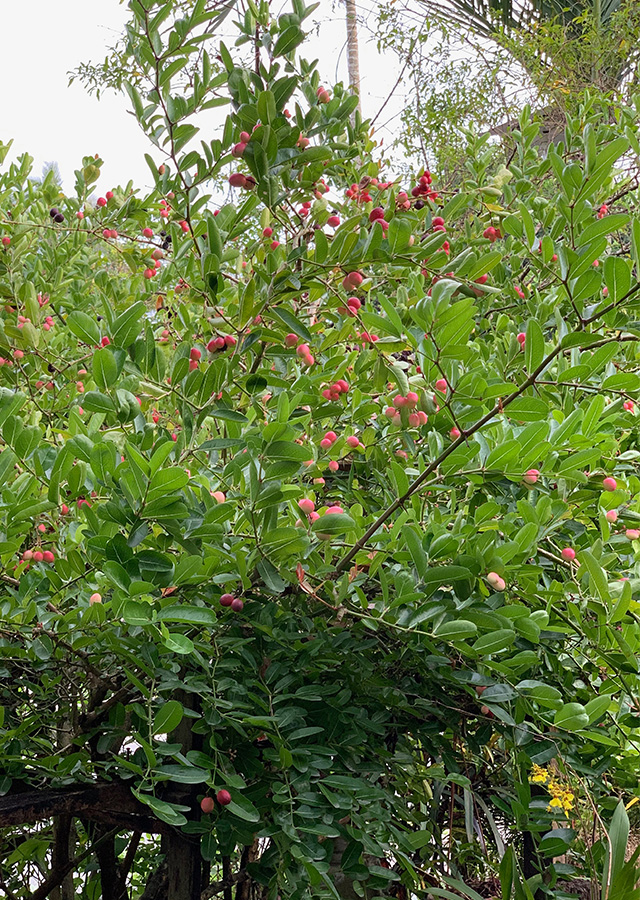
Lokasi di taman kami
Utama


Sinonim
Arduina carandas (L.) Baill.
Carissa salicina Lam.
Echites spinosus Burm.f.
Habitus
Semak. Perdu tahunan, tinggi mencapai 5 m
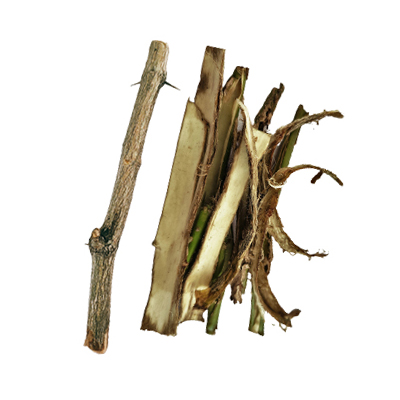
Bagian Yang Digunakan
Kulit Batang
Buah
Akar
Syarat Tumbuh
Matahari Penuh
Butuh Keteduhan
Habitat
Daratan
Penyebaran Tanaman
Buah renda menyebar dari Afganistan, India, Sri Lanka, China Selatan, Indo-China, Peninsular Malaysia dan berbagai daerah tropis lainnya. Tanaman ini memiliki sejarah panjang digunakan dalam sistem pengobatan tradisional, baik di Asia Selatan maupun Afrika. Dalam pengobatan Ayurveda, kulit batang digunakan untuk mengobati penyakit kulit sedangkan akarnya untuk gangguan kemih.
Nama Lokal
Kerendang (Betawi), Samarinda (Jawa), Senggaritan.
Agroekologi
Tumbuh baik pada tempat hingga ketinggian 1.800 m dpl. Tanaman ini cocok pada berbagai jenis tanah dan sering ditemukan di halaman. Menyukai tempat dengan curah hujan rata-rata 1.000-1.400 mm/th, pH tanah kisaran 6,5-8 dan sinar matahari penuh. Tanaman ini toleran terhadap kekeringan dan dapat beradaptasi pada suhu lingkungan yang tinggi.
Morfologi
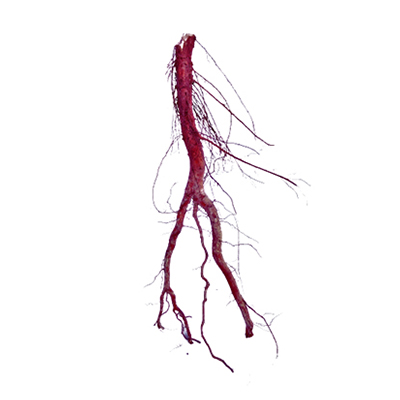
- Akar tunggang.
- Batang dahan berduri, langsing atau berbentuk garpu.
- Daun bentuk ovate berukuran 3-7 x 1,5-4 cm.
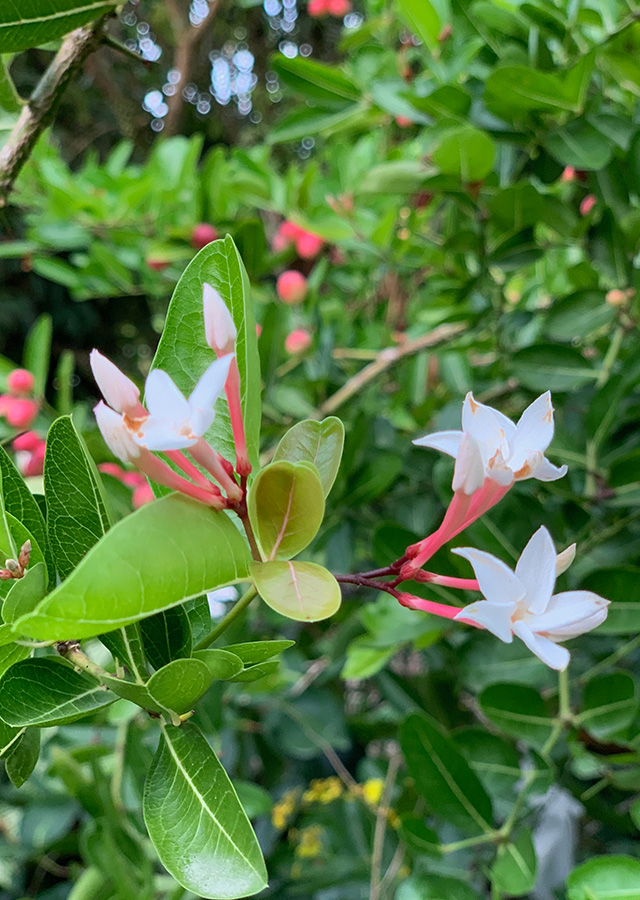
- Bunga beraroma wangi, mahkota berwarna putih, kelopak warna merah muda.
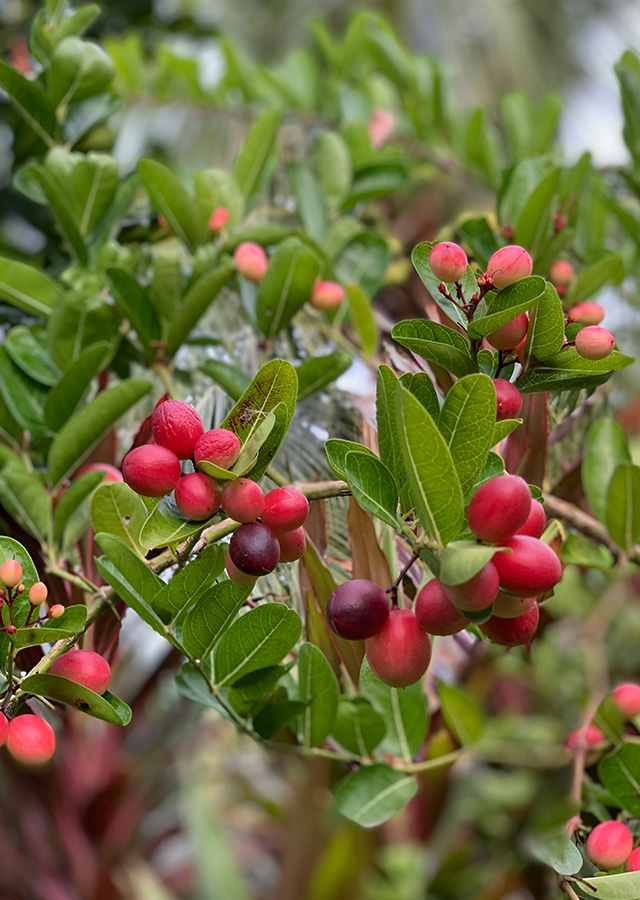
- Buah berry berbentuk elips berukuran 1,5-2,5 x 1-2 cm. Jika buahnya ungu kehitaman menunjukkan buah sudah sangat ranum, banyak getahnya, rasanya manis.
Budidaya
- Perbanyakan secara vegetatif (stek batang, cangkok) maupun generatif (biji). Biji berasal dari buah tua berwarna hitam keunguan.
- Pisahkan biji dan daging buah, kemudian jemur biji di bawah sinar matahari. Setelah kering, tanam biji di media tanah yang subur.
Kandungan Bahan Kimia
Alkaloid, fenolik, flavonoid, saponin, tanin, 2-acetyl phenol, lignan, carinol, sesquiterpenes (carissone, carindone), lupeol, β-sitosterol, 16 β-hydroxybetulinic acid, α-amyrin, glycoside, desnmethylnoracronycine, triterpenoid, carisol, linalool, β-caryophyllene, carissic acid, ursolic acid, ascorbic acid.
Khasiat
Mengobati sariawan, demam, asma, cacingan, penyakit kulit, batuk, gangguan kantung empedu, mencegah diare, sakit telinga.
Simplisia
Belum tersedia.
Bagian Tanaman Yang Dimanfaatkan
Ramuan Tradisional
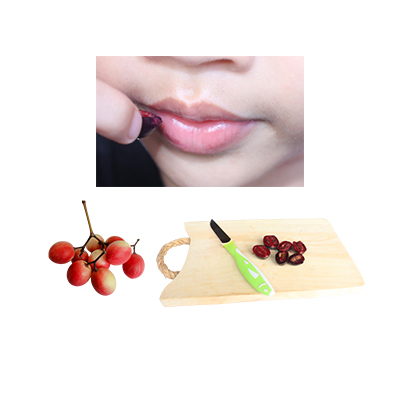

1. Sariawan
- Siapkan buah renda yang segar dan sudah tua.
- Belah buah dan oleskan pada bagian yang sakit.
- Ulangi pemakaian beberapa kali hingga sembuh.
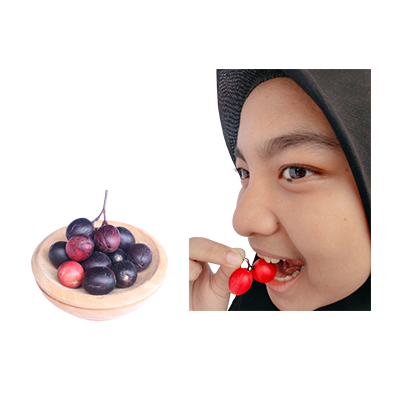

2. Penyakit kantung empedu
- Pilih buah renda yang segar, cuci hingga bersih dan tiriskan.
- Makan buah renda sebanyak 4 g sehari untuk membantu mengurangi sakit kantung empedu.
Sumber Referensi
- Grow Plants.(No date). Karonda plant. https://www.growplants.org/growing/karonda. 02-11-2020.
- Stuartxchange. (2019). Philippine Medicinal Plants. Karanda. http://www.stuartxchange.org/Caranda. 03-08-2020.
- Fern, Ken. (2019). Useful Tropical Plants. Carissa carandas. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Carissa+carandas. 03-08-2020.
- Virmani,R., Virmani,T., & Singh, C., et all. (2017). Hidden Potential of Natural Herb Carissa Carandas (Karonda). Research in Pharmacy and Health Sciences Vol 3(2): 294-302. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315811584_Hidden_Potential_of_Natural_Herb_Carissa_Carandas_Karonda. 03-08-2020.
- Badan penelitian dan pengembangan kesehatan.1997. Inventaris tanaman obat indonesia (IV). depkes RI.
- Herbpathy.com. https://herbpathy.com/Uses-and-Benefits-of-Carissa-Carandas-Cid395615-08-2020
- Longdom.org. http://longdom.org/Tradisionaluses,pharmacologicalactionandphytochemicalanalysisofCarissacarandasLinn:areview 05--12-2020
- Jayakumar K, Muthuraman B. 2018. Traditional uses and nutrient status of Indian native plant fruit (Carissa carandas Linn.). World Scientific News 96:217-224.
- Kumar V, Tarpada P, Sadariya K, Goswami S. 2017. Comparative phytochemical and antioxidant activities of methanol and petroleum ether extract of Carissa Carandas leaves, fruit and seed. Vivechan International Journal of Research 8(2).
- Singh A, Uppal GK. 2015. A review on Carissa carandas – phytochemistry, ethno-pharmocology, and micr
- Badan penelitian dan pengembangan kesehatan.1997. Inventaris tanaman obat indonesia (IV). depkes RI.