Hedge Row Tetracera
Tetracera indica (Christm. & Panz.) Merr.
Dilleniaceae
Location in our garden
Principal



Synonym
Assa exotica Gmel.
Assa indica Houtt. ex Christm. & Panz.
Eleiastis laevis Raf.
Habitus
Climbers. Annual vine, growing up to 5 m high
Part Used
Leaves
Roots
Stem
The Whole Plant
Young Shoot
Growing Requirements
Full Sunshine
Habitat
Forest
Shrublands
Terrestrial
Overview
Come from Southeast Asia Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia. The plants are used as sandpaper for smoothing wood and for polishing metal. The young, flexible and tough stems can serve as rough straps. Tetracera is one of the plants that has been used as a traditional medicine to treat various diseases. This plant can also be used as a medicine for people with diabetes mellitus and people with bad breath, but it is not stated which parts of this plant can be used to treat these diseases.
Vernacular Names
Rotsukhon daeng (Thai), Chặc chìu ấn (Vietnamese).
Agroecology
A small shrub in open places; a low liana, climbing over low shrubs, in brushwood and open forest at elevations from sea-level to 600 m.
Morphology
- Roots - tap root.
- Stems - woody, round stem shape, rough stem surface and slightly peeling, not gummy.
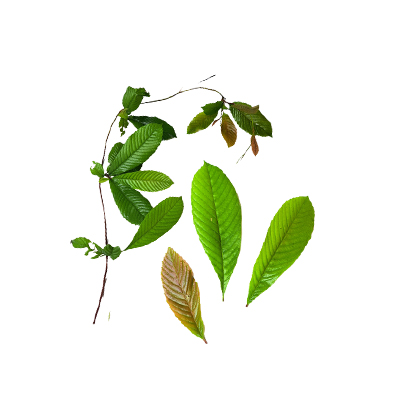
- Leaves - single, leaf color is dark green, sparse shape, leaf surface is slightly hairy, leaf margin (margofolio) is serrated (serratus), leaf veins appear (protrude) secondary parallel, leaf base is pointed, leaf tip is tapered, leaf stalk is slightly hairy, leaf sits (phylotaxis) alternating.
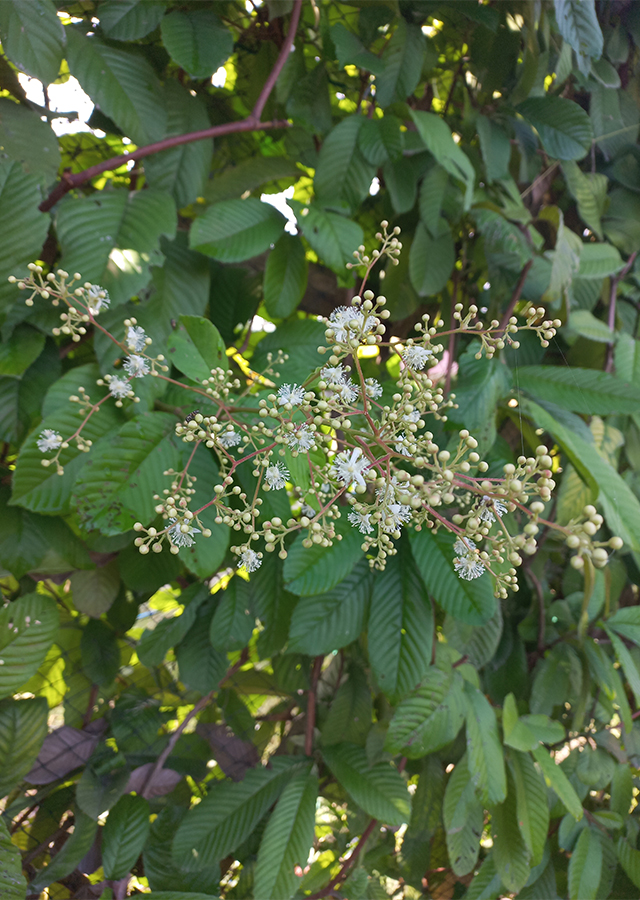
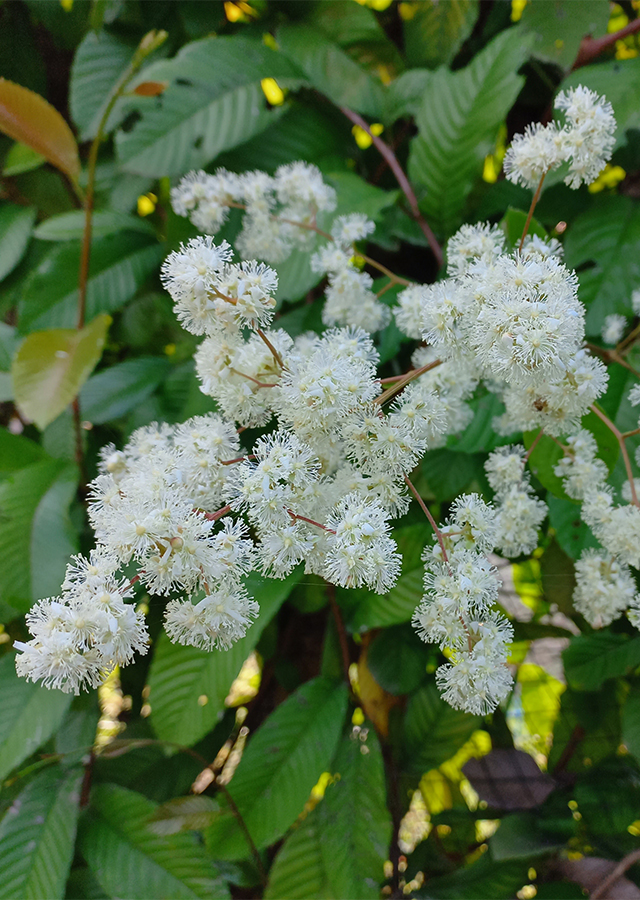
- Flowers - It has 3-5 petals, 3-4 carpels and pink colored stamens that form like pom-poms (2.5-3 cm in diameter). Flowers in clusters of 4-7 flowers, emerging from the terminal stem 5-8 cm long.
- Fruits - rough, round or oval with a diameter of 0.8-1 cm, bright red, shiny.
- Seeds - ovoid, covered with red fleshy tissue (arils).
Cultivation
Propagated by seeds and division of suckers.
Chemical Constituents
Compounds (phenolic) chloroacetic acid, phenol, 2, 6-dimethoxy and pyrocatechol. Flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin, myrisetin, rhamnetin, isorhamnetin and azaleatin).
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- In Malaysia, the roots are boiled and the water is drunk to reduce high blood pressure and body temperature when attacked by hot fever.
- The leaves are used as a powder medicine to relieve skin itching.
- An infusion of the shoots is used in the treatment of pulmonary haemorrhages
- An infusion of the shoots is used as a gargle for the treatment of mouth ulcers.
- The finely crushed young shoots are made into a poultice and put on bites of poisonous snakes and festering fingers.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Useful Tropical Plant Database. 2021. Tetracera indica. https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Tetracera+indica. 26-06-22.
- Royal Botanical Garden. 2021. Plant of the World Online : Tetracera indica (Christm. & Panz.) Merr. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:317418-1. 26-06-22.
- Plant Resources of South East Asia. 2017. Tetracera indica. https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Tetracera_indica_(PROSEA). 26-06-22.