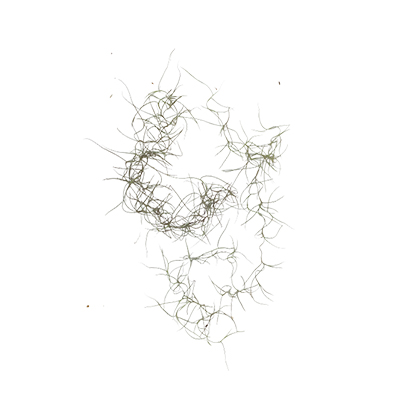
Spanish Moss
Tillandsia usneoides (L.) L.
Bromeliaceae
Location in our garden
Green House



Synonym
Dendropogon usneoides (L.) Raf.
Tillandsia crinita Willd. ex Beer
Tillandsia trichoides Kunth
Habitus
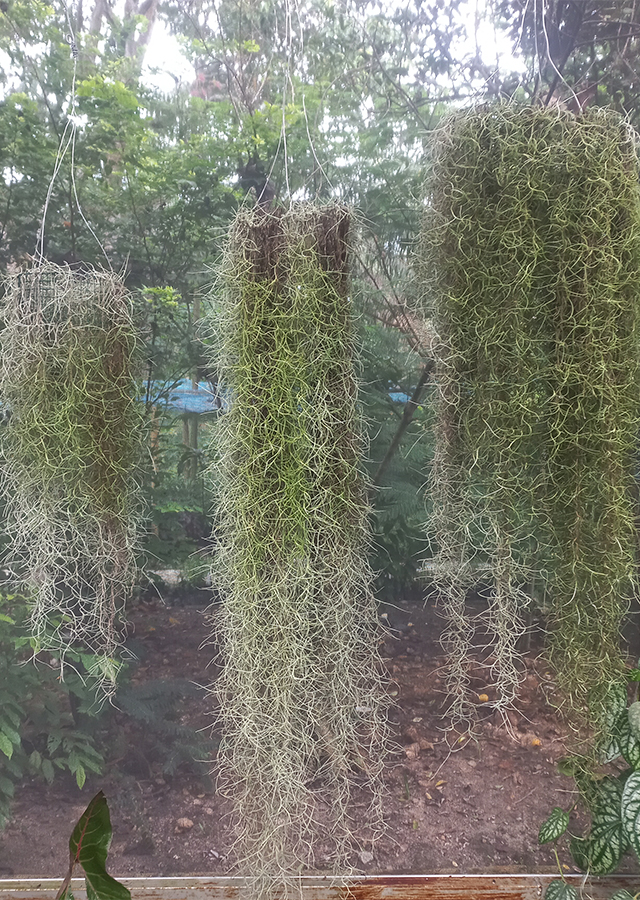
Herbaceous. A pendant, epiphytic, evergreen shrub hanging down from the branches of trees etc and growing around 6 m long
Part Used
The Whole Plant
Growing Requirements
Need Shade
Habitat
Riverbanks
Forest
Overview
Tillandsia usneoides is native to most of Mexico, Bermuda, Bahamas, Central America, South America, Southern United States, West Indies. This species has been naturalized in Queensland, Australia. Tillandsia usneoides is often grown as an ornamental plant in the tropics, it is also used as a packaging material and filler material, indicator plant, mulch, handicraft and decorative material, a source of elastic fiber, plaster or insulation material for the interior of the house (dry plant), food supplement and herbal medicine. Research has shown that Tillandsia usneoides accumulates mercury and is an indicator plant for detecting metallic pollutants or the presence of mercury in the atmosphere. By virtue of its function as a packaging and filling material, this species has long been used to fill mattresses, pillows, and car seats in the US and Europe, among other items. This species also produces strong elastic fibers that can be woven into mats, ropes and sacks. Tillandsia usneoides also has a long history and therapeutic potential. This species is believed and used traditionally as herbal medicine to treat various ailments.
Vernacular Names
Barbe grise (French), Heno (Italian), Adatima (Surinam).
Agroecology
Tillandsia usneoides can usually be found growing in many types of subtropical and tropical habitats. It is usually found hanging from the branches of trees, especially oaks and spruce. Prefers a moist, partially shaded position. The plant has a very sparse root system, mainly used for anchoring itself to the branches of trees. The plant absorbs most of its moisture and nutrients from the humid air of its environment, through the absorbent scale-coating of its leaves.
Morphology
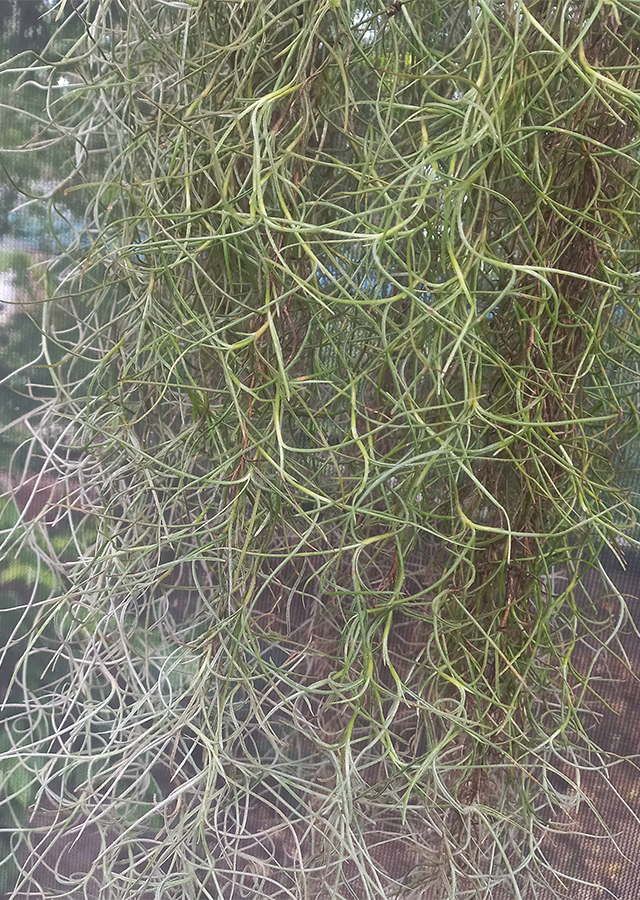
- Stems - thin and elongated like thread.
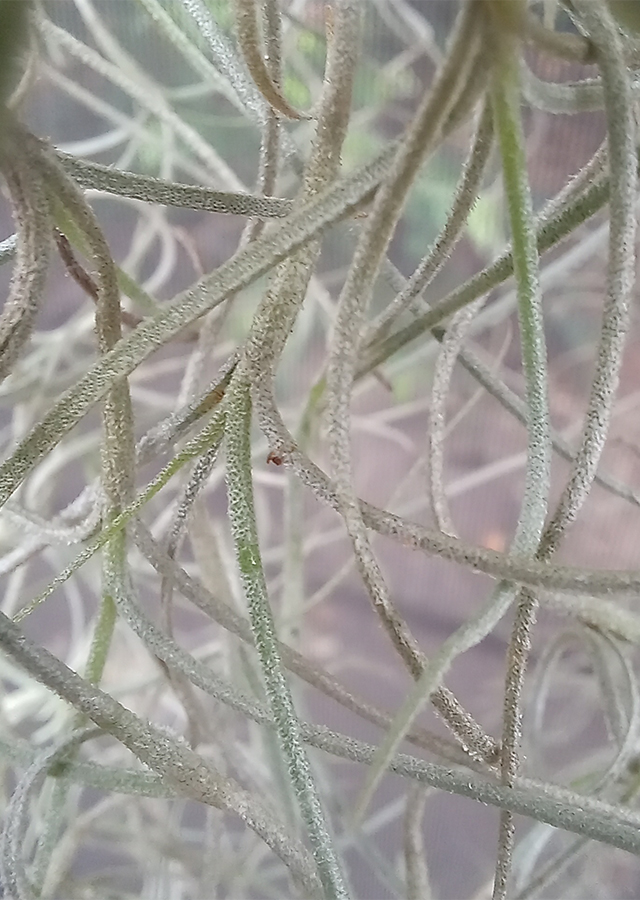
- Leaves - simple, unifoliate, scattered, thin, short (1.5 - 3 cm long, 0.1 - 0.2 cm wide) present in small clusters bent, narrow-linear, tightly covered with short silver to gray hairs known as trichomes. Hair helps absorb moisture and nutrients from the air. Leaves are silver to gray when dry, but light green when wet. Leaf edges are flat, leaf tips are pointed (acute), leaf bases are cut or truncate.
- Flowers - small, pale green or blue in color and most fragrant at night, the flowers appear solitary in the axils of the leaves. In cultivation, they rarely produce flowers.
Cultivation
- Propagated by division and stem cuttings (break the stem and replant it).
- Including plants that are easy to grow. Simply hang the plant in partial shade and mist it regularly with warm water.
Chemical Constituents
Cycloartane triterpenoids, cycloarterenol, 4,5-dihydroxy-3',7-demthoxyflavanone, mixed steroids stigmasterol, -sitosterol, campesterol, 26 cycloartane derivatives ((22E)-25,26,27-trisnor-3-oxocycloart-22- en-24-al, (24E)-3-oxocycloart-24-en-26-al, 24-hydroxycycloart-25-en-3-one, (23E)-25-methoxycycloart-23-en-3-one, (23E)-25-hydroperoxycycloart-23-en-3-one, 25,26,27-trisnor-24-hydroxycycloartan-3-one, methyl (24E)-26-carboxy-3,4-seco-cycloart-4 (29),24-dien-3-oate, methyl (23E)-25-hydroxy-3,4-seco-cycloart-23-en-3-oate, methyl (23E)-25-methoxy-3,4- seco-cycloart-23-en-3-oate, and methyl 24-hydroxy-3,4-seco-cycloart-25-en-3-oate), carotenoids, tocotrienols, flavonoids, alkaloids, polycarpol 3-hydroxy-methylglutaric acid (HMG).
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- In south Louisiana, has been reportedly used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
- In Bahia, Brazil, decoction of the whole plant, "Sambambaia," is used for sexual weakness.
- In the Guianas, whole plant used to strengthen and make the hair more attractive.
- Surinam Arawak steep the plant in hot water until decompossed, and use the liquid to wash their hair to achieve a glossy shine.
- In the French Guiana juice of a tillandsia used to treat rheumatism.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Royal Botanic Gardens. Plant of the World Online: Tillandsia usneoides (L.) L. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:1169665-2. 26-06-22.
- Stuartxchange. 2018. Philippine Medicinal Plants: Buhok ni Ester. http://www.stuartxchange.org/BuhokNiEster. 26-06-22.
- Tropical Plants Database, Ken Fern. 2021. Tillandsia usneoides. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Tillandsia+usneoides. 26-06-22.
- Flora Fauna Web. 2021. Tillandsia usneoides (L.) L. https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/2/5/2515. 26-06-22.
- WholisticMatters. 2019. The Antioxidant Benefits of Spanish Moss. https://wholisticmatters.com/the-antioxidant-power-of-spanish-moss/#:~:text=Tillandsia%20usneoides%20. 26-06-22.
- E Estrella-Parra, M Flores-Cruz, G Blancas-Flores, SD Koch, FJ Alarcón-Aguilar. 2019. The Tillandsia genus: history, uses, chemistry, and biological activity. Bol Latinoam Caribe Plant Med Aromat 18 (3): 239 – 264.